Adding Authorization to A Node.js Application
Jun 30th, 2022

Roie Schwaber-Cohen
Authorization |
Engineering

The main goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate adding authorization to a Node.js application with Aserto’s Express SDK.
This tutorial has three parts:
- Authorization with Aserto - where we’ll learn about how authorization with Aserto works and set up and review our authorization policy
- Setting up a Node.js server - where we’ll set up a Node.js server that will be used as the backend for our Todo application
- Adding authorization - where we’ll add the authorization middleware to our Node.js server
Prerequisites
You should have Node.js and Yarn or NPM installed on your machine to use the test application that accompanies this tutorial.
Authorization - quick overview
Before we get started with building the policy, let’s talk about how the authorization process takes place. At the heart of the authorization process is the Authorizer, where authorization decisions get made.
There are three inputs that contribute to an authorization decision:
- the identity context: the actor that is taking the action. Our application will resolve the user’s identity after they have logged in, and pass that identity to the server with every request.
- the resource context: the resource that is being acted upon. In our Todo application, the resource is each todo item - and particularly information about the owner of each todo item.
- the policy context: the rules should be applied to make the authorization decision. Policies can be stored either as OCI images or as code in GitHub or GitLab. A policy consists of multiple policy modules that correspond to the endpoints that are being protected. Our server will be set up with middleware that will resolve which policy module should be invoked for a given request.
In this tutorial, we’ll build a set of policy modules and see how they govern the authorization behavior of an application.
Design
The application we’ll add authorization to is a classic Todo application. We’ve all seen those before: Users can create a todo, mark it as complete or delete it. In this tutorial, we’ll limit the abilities of different types of users and check whether or not they are permitted to take specific actions.
Users can be grouped by the set of permissions they will be granted. We call these groups “roles”. In this tutorial, we’ll have three roles:
- A “viewer” - will be able to only view the todo list
- An “editor” - will be able to view the todo list, add a todo item, and delete or complete a todo item they have previously created.
- An “admin” - will be able to do all of the above, but also be able to complete and delete any todo item.
As we mentioned before, we need to establish the identity of a user in order to determine what actions they may perform. So we’ll need to have some way of authenticating them in the first place.
Every todo item will be saved in the database including an identifier of the user who created it. We’ll use this information to determine whether the currently logged in user is allowed to perform an action on any of the todo items. We’ll also use it to display a profile image of the user in the todo list, so we can tell which user created a particular todo item.
Getting started with Aserto
In this part of the tutorial, we’ll spend some time interacting with the Aserto console. To get started, log in to your Aserto account (if you don’t already have an Aserto account, sign up here). In the console, we’re going to connect to a demo identity provider and create a policy instance.
Add the Demo Citadel IDP
In order to understand how the authorization process works, we’ll need to add an identity provider. For the purposes of this tutorial, we’ll use the Demo Citadel IDP, which is a sample identity provider that we created for you. It includes 5 users with different roles and attributes you can use to test your policies (when you’re ready to go to production, you’ll be able to use Auth0 or Okta as your IDP).
To set up the Citadel IDP, head to the “Directory” tab and click “Connect an identity provider”.

Select "Demo Citadel IDP", and name the connection "Citadel". Use the display name "Citadel" and click “Add connection”.
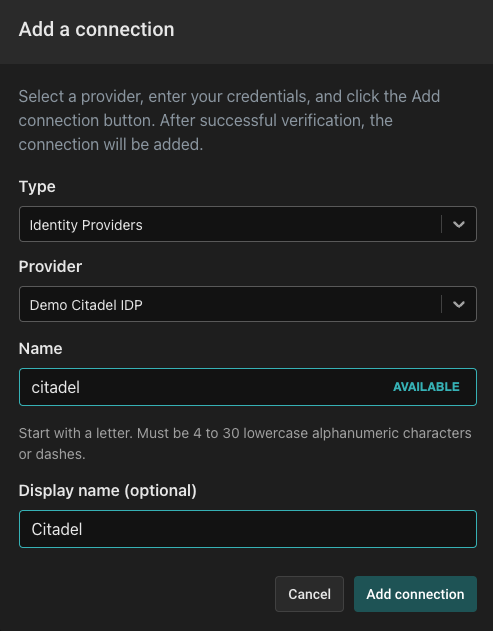
The Directory tab will now be populated with the users from the Demo Citadel IDP.
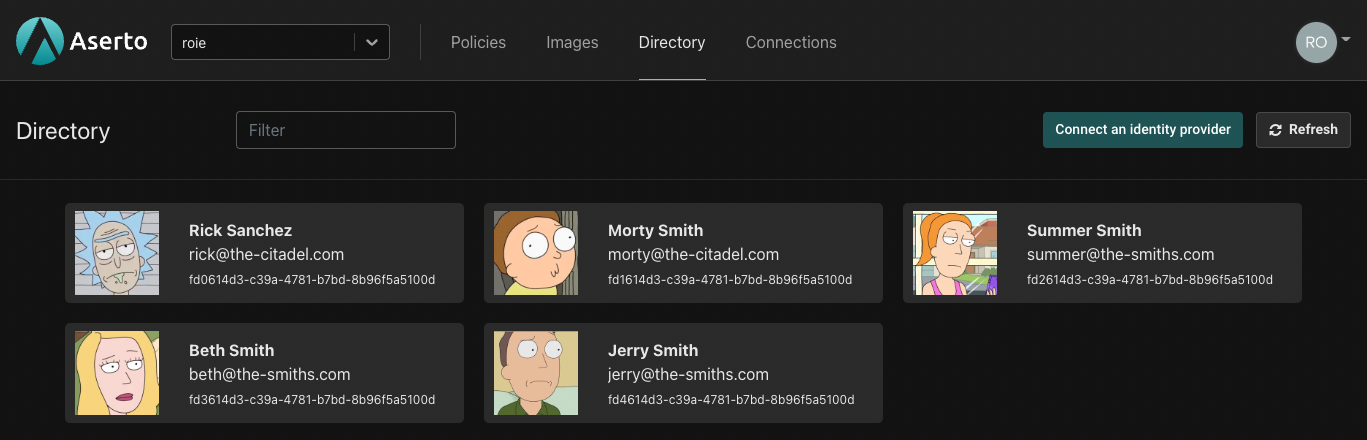
Next, we want to set up the policy that will determine how authorization decisions are going to be made. For the purpose of this tutorial, we have created a policy that you can easily load into your Aserto tenant.
Review and test the todo policy
Navigate to the Policies tab and open the "todo" policy instance (This policy instance is created automatically for you when you sign up). A policy instance is a running instance of the authorizer, attached to a particular policy image (you can create policy images in the Images tab).
Policies in Aserto are comprised of multiple modules, which correspond to the endpoints that require authorization. Click on the "Modules" sidebar button and review the five policy modules in the todo policy.
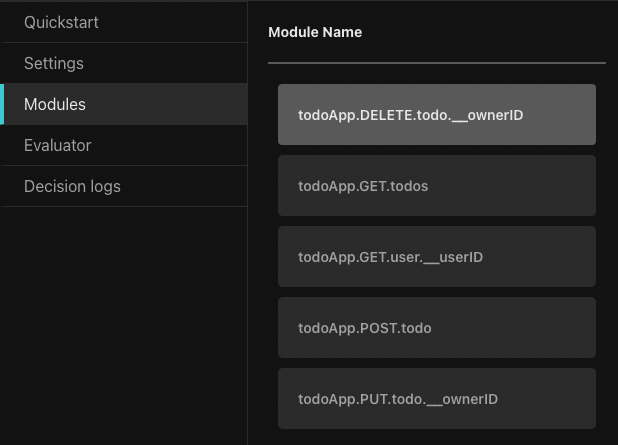
Policy modules are named using the following convention:
<policy-root>.<http-verb>.<path>.[<__parameter>]The policy modules each begin with the root name of the policy (in this case todoApp). They correspond to the application routes, for example, the GET /todos route corresponds to the todoApp.GET.todos policy module. As we’ll see later, when a request is made to the authorization middleware, it will resolve the policy module for the request based on the policy module name.
Policy modules may also have a reference to a parameter on an endpoint, which is denoted by the __ followed by the name of the parameter.
For example, the PUT /todo/:ownerID path uses the parameter ownerID and will be available to the policy module todo.PUT.todo.__ownerID as part of the resource context. We’ll see how this is used in practice a bit later.
The authorization policies
As we mentioned before, authorization policies are written in Rego, which is a higher-level language that was inspired by Datalog.
Let’s take a look at the simplest policy module: todoApp.GET.todos.
package todoApp.GET.todos
default allowed = trueThis policy module allows all requests to the GET /todos route since we want any user to be able to view the todo list.
Now let’s take a look at the next policy module, todoApp.POST.todo:
package todoApp.POST.todo
import future.keywords.in
import input.user
default allowed = false
allowed {
allowedRoles := {"editor”, “admin” }
some x in allowedRoles
user.attributes.roles[_] == x
}There’s a lot more going on in this module. First, we import the future.keywords.in keyword. This allows us to use the in keyword in our policy (we’ll see how it’s used in a moment).
We also import input.user, which will allow us to refer directly to the user object in our policy without referencing the full path input.user. Aserto makes this user object available to the policy, and it represents the resolved identity of the user that is making the request.
Next, we have the default allowed = false line. We want to ensure that if the conditions in the allowed clause aren’t met, the decision will be false.
Finally, we can see the allowed clause. To understand how it works, let’s first take a look at the user input object (shortened here for brevity):
{
"id": "fd0614d3-c39a-4781-b7bd-8b96f5a5100d",
"email": "rick@the-citadel.com",
"picture": "https://github.com/aserto-demo/contoso-ad-sample/raw/main/UserImages/Rick%20Sanchez.jpg",
"identities": {
...
},
"attributes": {
...
"roles": [
"admin",
"evil_genius",
"grandpa",
"squanch"
]
},
...
}The user.attribute.roles referenced in the policy points to the list of roles under the attributes property in the user object.
The expression some x in allowedRoles is effectively a for-each loop that iterates over the roles in the allowedRoles list we defined. The x variable is the current role in the loop. The expression user.attributes.roles[_] = x iterates over each role in the roles list found in the user object (under attributes), and checks if any of them matches the current role x. So, if one of the user roles matches one of the allowedRoles, the allowed decision will be true.
To test this policy module, we’ll head to the Policy Evaluator. In the Policy Evaluator, we can check what the authorization decision will be for a given user and policy module.
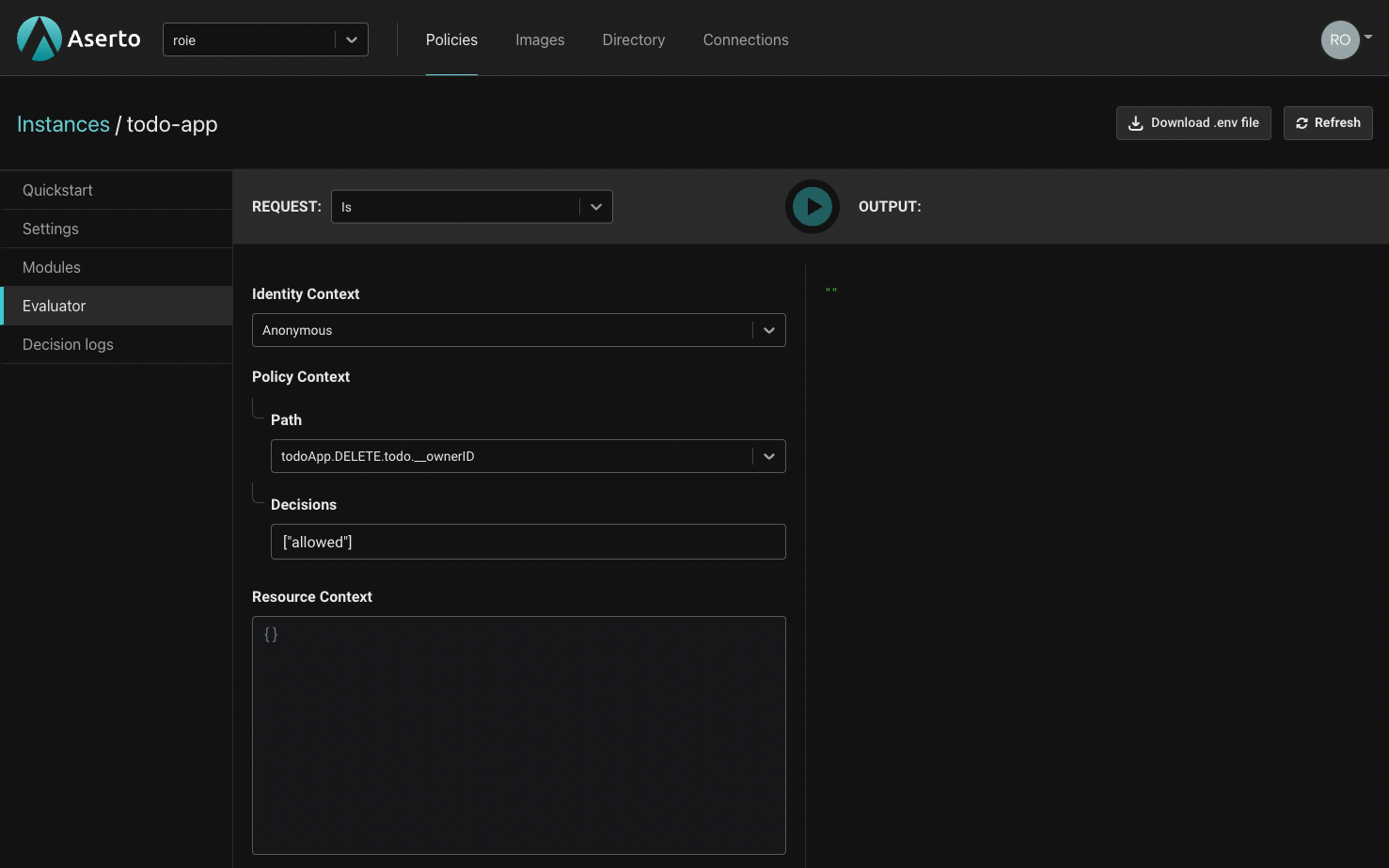
For the identity context dropdown, we have three options: We can make an “anonymous” evaluation, where no identity will be provided. Alternatively, we can pass a JWT which will be decoded by the evaluator. Finally, we can pass a “Subject” which will let us select one of the users in our directory.
We’ll select "Rick Sanchez" and set the Path of the policy module to be evaluated to todoApp.POST.todo.
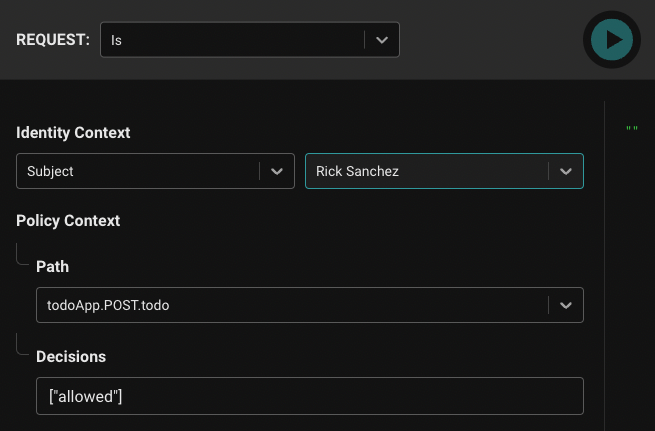
Rick is an “admin” so we’ll expect the todoApp.POST.todo policy module’s allowed decision to be true.
{
"decisions": [
{
"decision": "allowed",
"is": true
}
]
}Now let’s test this policy module with a user whom we know shouldn’t be able to create a todo - Jerry Smith. As you can see below, he doesn’t have any of the roles required by the todoApp.POST.todos policy module.
{
"id": "fd4614d3-c39a-4781-b7bd-8b96f5a5100d",
"display_name": "Jerry Smith",
...
"identities": {
...
},
"attributes": {
...
"roles": [
"viewer",
"dad",
"looser"
],
},
...
}Let’s re-evaluate the todoApp.POST.todo policy module for Jerry. We’ll set the identity context to “Subject” and select "Jerry Smith". This time, the result will be:
{
"decisions": [
{
"decision": "allowed",
"is": false
}
]
}The package name for the todo.PUT.todo.__ownerID module is:
package todo.PUT.todo.__ownerIDThis naming convention indicates that the parameter `ownerID` will be attached to the resource context. The same is true for the todo.DELETE.todo.__ownerID policy module.
Next, let’s examine the body of both of these policy modules since it's identical. For these two policy modules, we’re going to leverage the resource context in order to determine whether or not a user owns the todo entry they are trying to delete or update.
import future.keywords.in
import input.user
import input.resource
default allowed = false
allowed {
user.attributes.roles[_] == "editor"
some id , _ in user.identities
id == resource.ownerID
}
allowed {
user.attributes.roles[_] == "admin"
}Similar to the previous modules, we import the in keyword and the user input object. This time, we also import the resource input object.
Let’s consider the following user:
{
"id": "fd1614d3-c39a-4781-b7bd-8b96f5a5100d",
"enabled": true,
"display_name": "Morty Smith",
"email": "morty@the-citadel.com",
"picture": "https://github.com/aserto-demo/contoso-ad-sample/raw/main/UserImages/Morty%20Smith.jpg",
"identities": {
"+1-844-667-3743": {
"kind": "IDENTITY_KIND_PHONE",
"provider": "",
"verified": false
},
"CiRmZDE2MTRkMy1jMzlhLTQ3ODEtYjdiZC04Yjk2ZjVhNTEwMGQSBWxvY2Fs": {
"kind": "IDENTITY_KIND_PID",
"provider": "local",
"verified": true
},
"morty": {
"kind": "IDENTITY_KIND_USERNAME",
"provider": "",
"verified": false
},
"morty@the-citadel.com": {
"kind": "IDENTITY_KIND_EMAIL",
"provider": "local",
"verified": true
}
},
"attributes": {
…
"roles": [
"brother",
"editor",
"grandson",
"little_helper",
"sidekick",
"son"
],
…
},
…
}As you can see, Morty is an editor and not an admin, so the first allowed clause will apply to him. This allowed clause introduces another for-each loop. This time, we are iterating over the keys of the user.identities object. The following expression:
some id , _ in user.identities
id == resource.ownerIDmeans that we will compare each of the keys in the user.identities object to resource.ownerID which comes from the resource input object. The resource input object is attached to any request where resourceContext is passed. In our case, the Aserto middleware will take the parameter passed to this path (ownerID) and attach it to the resourceContext.
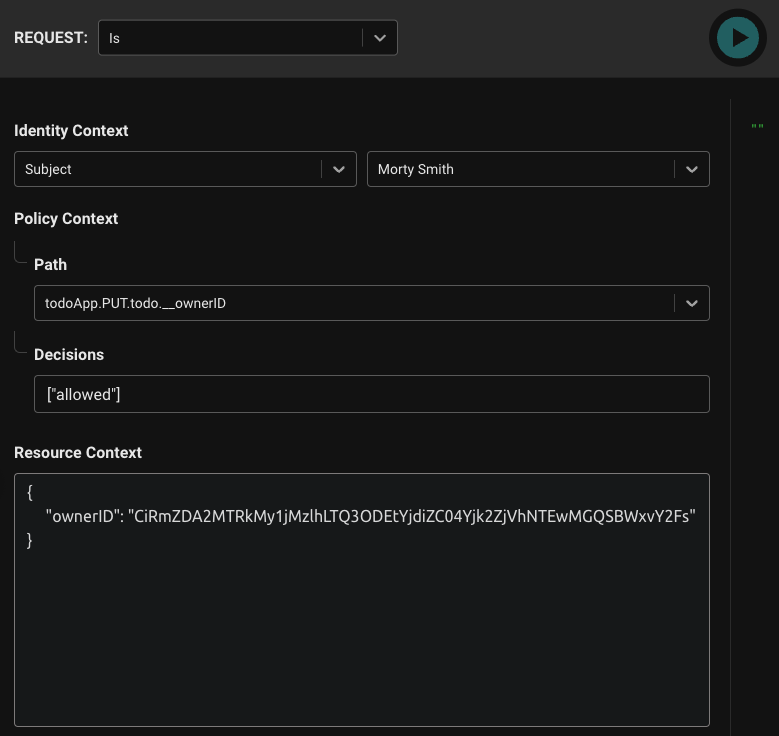
When we evaluate these policy modules, we’ll now pass the resource context as well. First, let’s test a scenario where the allowed decision will be false: We’ll set the Subject to be "Morty Smith" and set the resource context with Rick’s identifier:
{
"ownerID": "CiRmZDA2MTRkMy1jMzlhLTQ3ODEtYjdiZC04Yjk2ZjVhNTEwMGQSBWxvY2Fs"
}
The result of this evaluation will be:
{
"decisions": [
{
"decision": "allowed",
"is": false
}
]
}This is because Morty can’t delete a todo entry that doesn’t belong to him. Let’s change the ownerID to match his own identifier (note: the identifier might look similar to Rick’s identifier, but they are different):
{
"ownerID": "CiRmZDE2MTRkMy1jMzlhLTQ3ODEtYjdiZC04Yjk2ZjVhNTEwMGQSBWxvY2Fs"
}Now the result will be:
{
"decisions": [
{
"decision": "allowed",
"is": true
}
]
}as we expected.
Now that we have a good understanding of how the policy module works, let’s move on to getting our Node.js server set up, and then adding authorization to it using the Aserto Express middleware.
Setting up the Node server
If you want to add the authorization middleware to the application yourself, run the following command:
git clone --branch no-authorization git@github.com:aserto-demo/todo-node-js.gitOtherwise, you can download the completed version of the Node server located here and skip the steps for adding authorization.
Download the .env file
Before starting your server, head to the policy instance you created, and download the .env file generated for the policy instance:

Place the downloaded file in the root folder of your server and rename it to .env. Then, add the following lines to the file:
JWKS_URI=https://citadel.demo.aserto.com/dex/keys
ISSUER=https://citadel.demo.aserto.com/dex
AUDIENCE=citadel-appStart the Server
In the todo-server directory you just cloned, run the following commands:
yarn
yarn startThe server will start on http://localhost:3001.
Test
We can use curl to test the endpoints the server exposes. Note: These commands will work only for the version of the server without the authorization middleware in place.
Insert
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:3001/todo' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"ID": "id-test",
"Title": "todo-test",
"Completed": false,
"OwnerID": "sub-test"
}'Get
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:3001/todos'Update
curl --location --request PUT 'http://localhost:3001/todo/CiRmZDE2MTRkMy1jMzlhLTQ3ODEtYjdiZC04Yjk2ZjVhNTEwMGQSBWxvY2Fs' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"ID": "id-test",
"Title": "todo-test",
"Completed": true,
"OwnerID": "sub-test"
}'Delete
curl --location --request DELETE 'http://localhost:3001/todo/CiRmZDE2MTRkMy1jMzlhLTQ3ODEtYjdiZC04Yjk2ZjVhNTEwMGQSBWxvY2Fs' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"ID": "id-test",
"Title": "todo-test",
"Completed": true,
"OwnerID": "sub-test"
}'Get User
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:3001/user/CiRmZDE2MTRkMy1jMzlhLTQ3ODEtYjdiZC04Yjk2ZjVhNTEwMGQSBWxvY2Fs'Test the application and server
This demo includes two components: the Node.js server that serves our API, and the React application which consumes it.
The server should already be running, but if it isn't, run the following command in the todo-server directory:
yarn startNext, clone the todo-application from this repository:
cd ..
git clone git@github.com:aserto-demo/todo-application.gitNow install the application dependencies and start the application by running the following in the downloaded todo-application directory:
yarn
yarn startYour application and server are now both running, and your browser should now open the application on the http://localhost:3000 page, while the server will keep running on http://localhost:3001. You should now see the todo app.
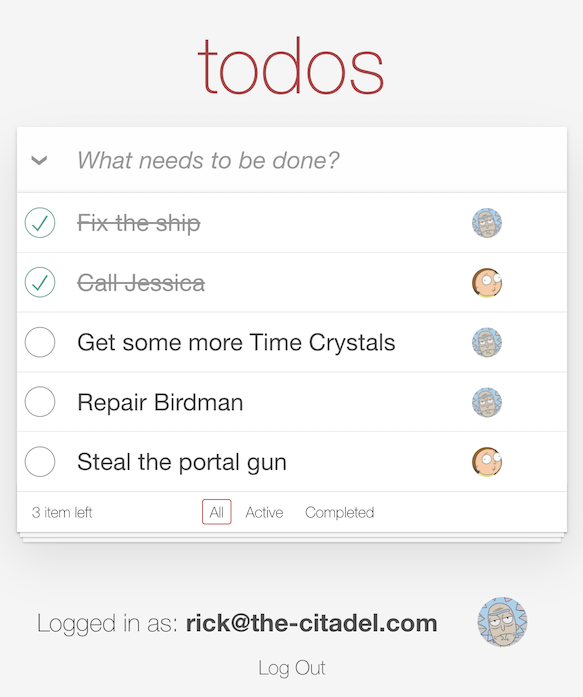
Start by logging in as the “admin” - rick@the-citadel.com and the password V@erySecre#t123!. You can add some todo items, then complete and delete some of them. Next, log in as the “editor” - morty@the-citadel.com using the same password. As you’ll see, because we didn’t plug in our authorization middleware just yet, you’ll be able to complete and delete any of the todo items - even ones that are not owned by morty@the-citadel.com. Of course, this isn’t the desired behavior - so let’s add authorization to the application.
Adding Authorization
We can now add authorization to our API endpoints. First, we’ll need to add the Aserto authorization middleware dependency to our project. In your command line, run:
yarn add express-jwt-asertoIn index.ts, add the following on line 7:
import jwt = require("express-jwt");
import jwksRsa = require("jwks-rsa");
import aserto = require("express-jwt-aserto");
const { jwtAuthz } = aserto;
We'll set up the checkJWT middleware, which will verify the validity of JWT tokens sent to our API:
const checkJwt: jwt.RequestHandler = jwt({
// Dynamically provide a signing key based on the kid in the header and the signing keys provided by the JWKS endpoint
secret: jwksRsa.expressJwtSecret({
cache: true,
rateLimit: true,
jwksRequestsPerMinute: 5,
jwksUri: process.env.JWKS_URI,
}),
// Validate the audience and the issuer
audience: process.env.AUDIENCE,
issuer: process.env.ISSUER,
algorithms: ["RS256"],
});We’ll create a configuration file that will read from the .env file.
const authzOptions = {
authorizerServiceUrl: process.env.ASERTO_AUTHORIZER_SERVICE_URL,
policyId: process.env.ASERTO_POLICY_ID,
policyRoot: process.env.ASERTO_POLICY_ROOT,
authorizerApiKey: process.env.ASERTO_AUTHORIZER_API_KEY,
tenantId: process.env.ASERTO_TENANT_ID,
};Next, we’ll initialize the Aserto middleware function.
//Aserto authorizer middleware function
const checkAuthz: express.Handler = jwtAuthz(authzOptions);Finally, we’ll add the checkJWT and checkAuthz middleware functions for each of our application routes. For example,
app.get("/user/:userID", async (req, res) => { ... }will now become:
app.get("/user/:userID", checkJwt, checkAuthz, async (req, res) => { ... }Repeat the process for each of the other routes.
Now, the checkAuthz middleware will pass the identity and resource contexts passed to it from the application and send it to the Aserto authorizer which will produce an authorization decision for each endpoint.
Testing the todo application with authorization
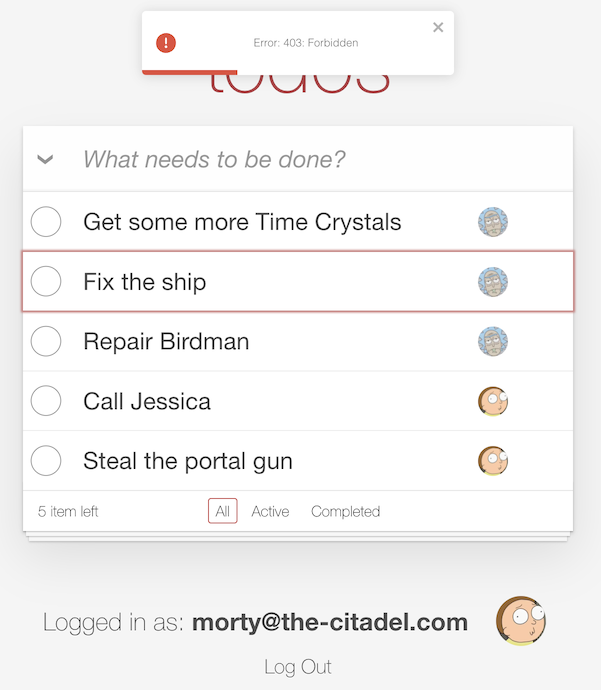
After making these changes, restart the Node server and refresh the application. You should already be logged in as Morty. You should be able to add a todo item, complete it, and delete it. If there are any of Rick’s todo items left, and you attempt to delete them as Morty, you should now see the following error:
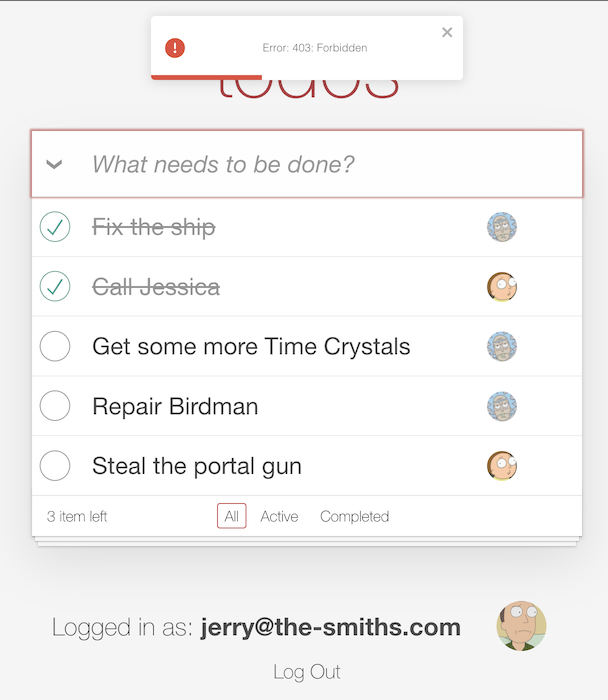
If you log in as Jerry (username: jerry@the-smiths.com, password: V@erySecre#t123!) and try to add a todo item, you should see the same error:
Finally, if you log in as Rick again (username: rick@the-citadel.com, password: V@erySecre#t123!) and try to delete the todo items that were created by Morty, you’ll see there are no errors.
Summary
In this tutorial, we learned about how Aserto authorization policies work and how to test them using the evaluator found in the Aserto console. We hope you found this tutorial useful and that you can use it to implement authorization with Aserto for your own applications.

Roie Schwaber-Cohen
Developer Advocate
Related Content

Why multi-tenant SaaS applications need real access control from day 1
Anyone who’s tried to retrofit multi-tenancy into a business application knows - it’s darn near impossible. You have to rebuild the app. We learned this time and again while at Microsoft, Splunk, HPE, and Puppet.
Jul 14th, 2022

Adding Authorization to A Python Application
In this tutorial, we'll learn how to add authorization to a Todo app written in Python, using the Aserto Python middleware.
Jul 21st, 2022

Adding Authorization to An ASP.NET Application
In this tutorial, we'll learn how to add authorization to a Todo app written in ASP.NET, using the Aserto ASP.NET middleware.
Aug 4th, 2022
&color=rgb(100%2C100%2C100)&link=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2Faserto-dev%2Ftopaz)